Learning check
Once you have watched the video, check your learning with this quiz.
The microscope
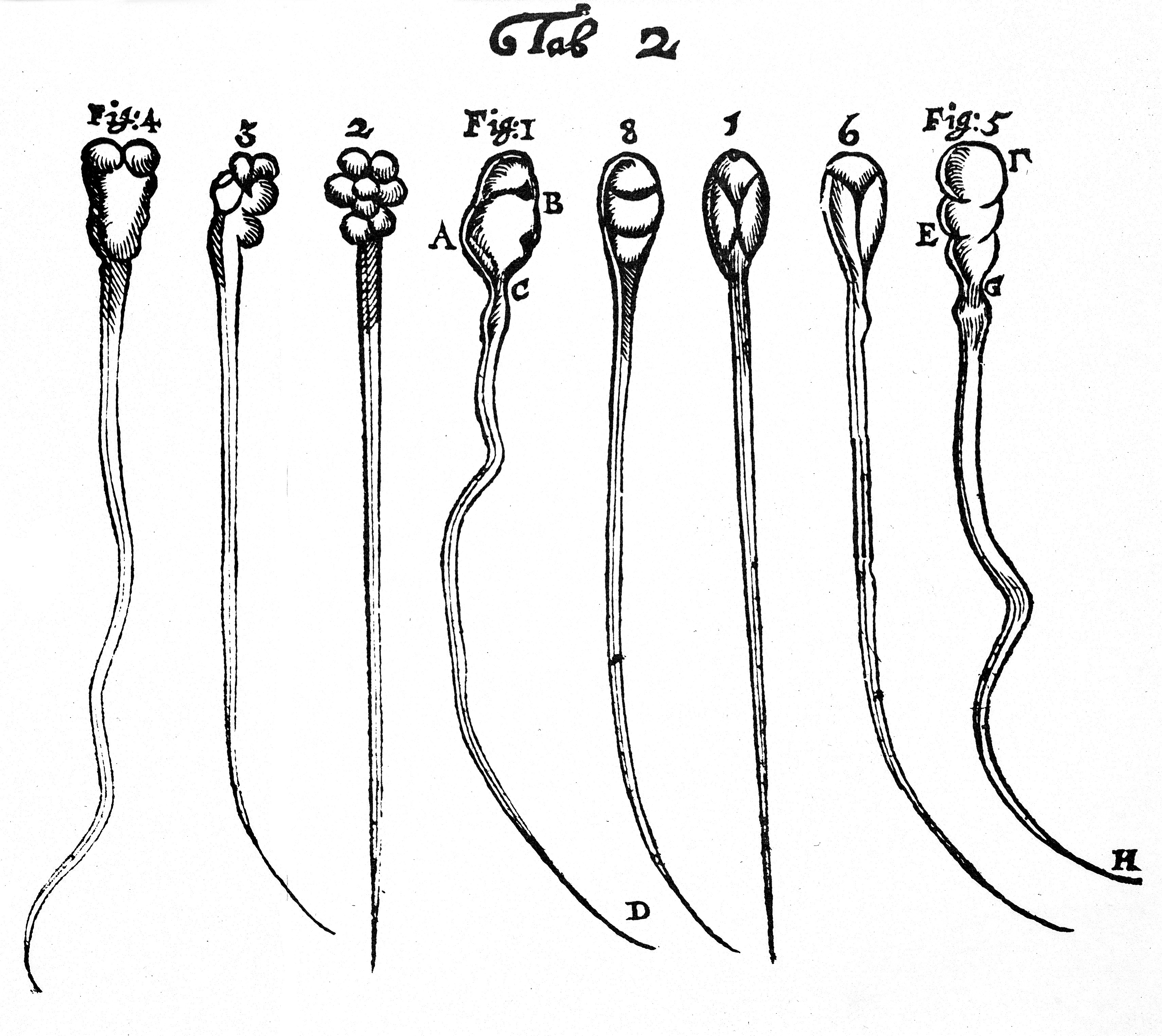
van Leeuwenhoek's microscope
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek is credited with constructing the first microscope.
- Size: matchbox
- Held close to the eye
- Magnification: 400x
van Leeuwenhoek was the first to describe sperm and (probably) bacteria, which he called "animalcules" ("little animals").
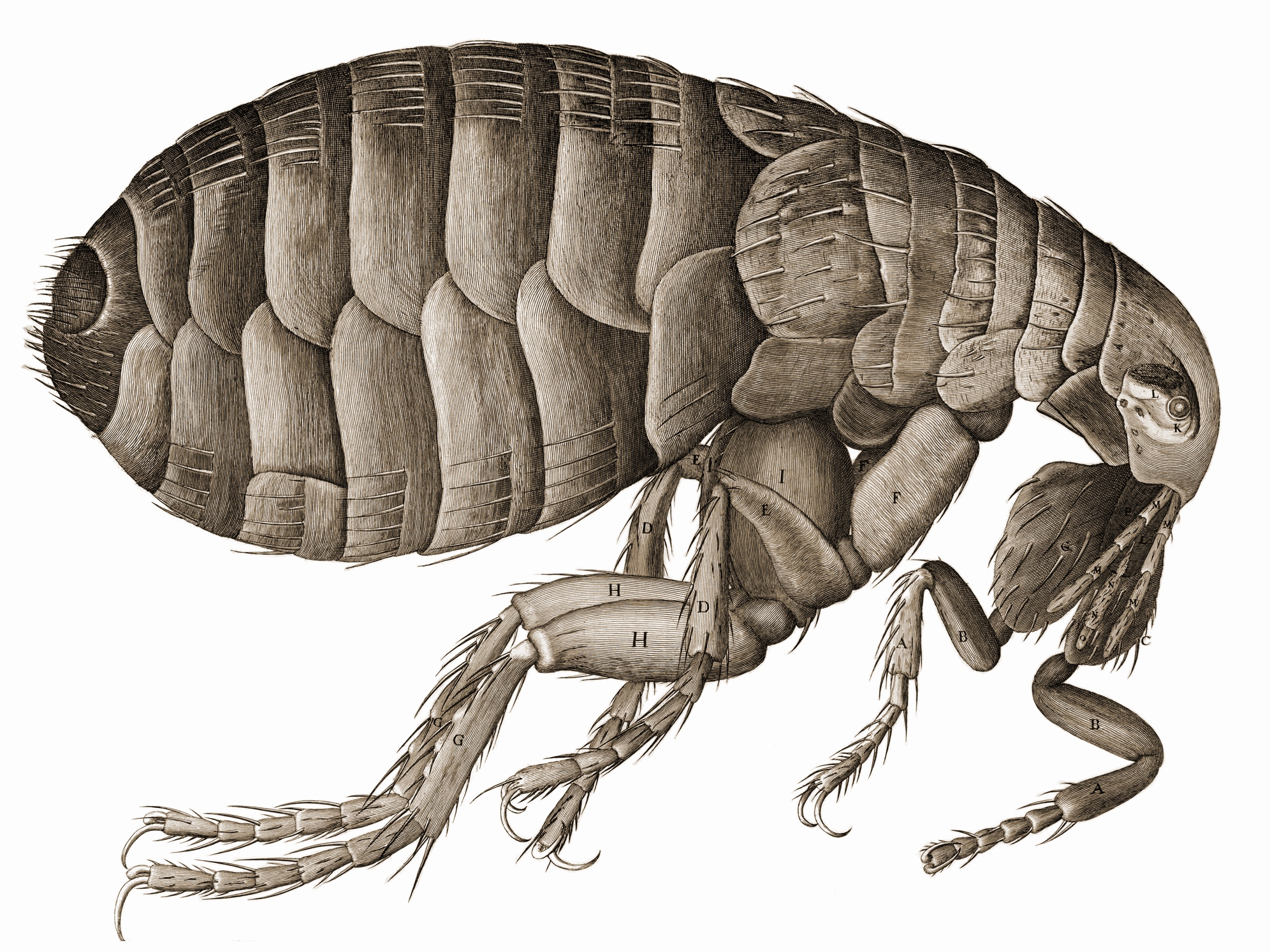
Hooke's microscope
 The light from an oil lamp (K) was focused on the specimen (M) with the help of a water-filled sphere (G).
The light from an oil lamp (K) was focused on the specimen (M) with the help of a water-filled sphere (G).
Hooke also drew what he saw through his microscope.
- Publishes "Micrographia" with detailed drawings of the "little life".
- Coins the term "cell"
In a sample from cork oak, Hooke sees what he describes looking like cells in a monastery. Although nobody at the time knew what a (biological) cell is, Hooke coined the term "cell".
What characterizes a cell?
All cells have
- a cell membrane,
- cytoplasm (fluid-like intracellular substance), and
- DNA (in one or several chromosomes).
What the cell theory says
- All organisms consist of one or more cells.
- The cell is the fundamental living unit.
- New cells may only arise from other cells.
Lipids
Lipids are a diverse group of fat or fat-like molecules, insoluble in water.
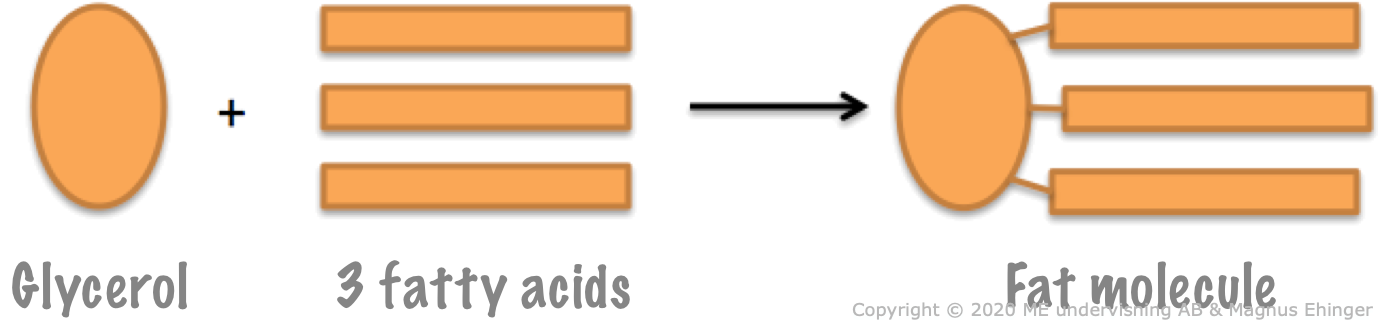 Fats are made of glycerol and fatty acids.
Fats are made of glycerol and fatty acids.
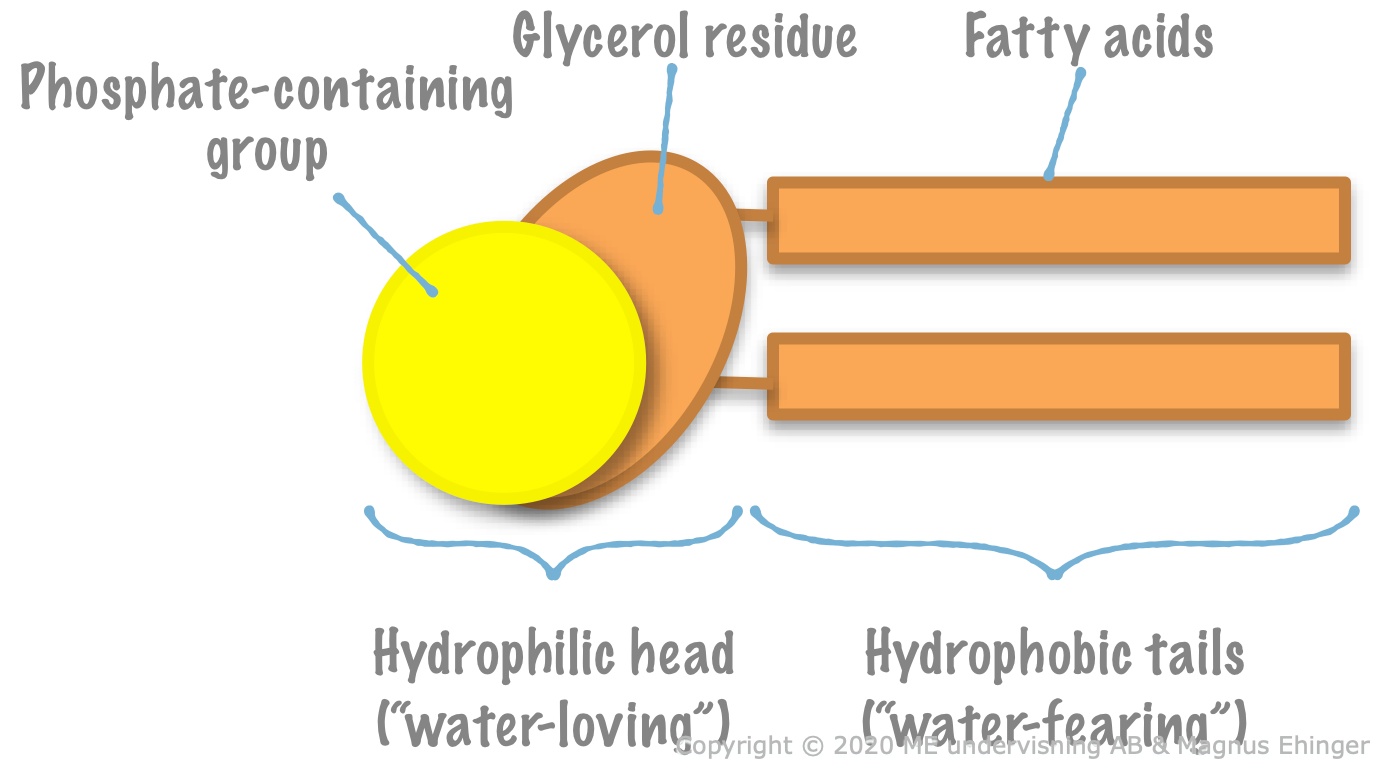 Phospholipids have a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails.
Phospholipids have a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails.
Cell membranes are made of phospholipids.
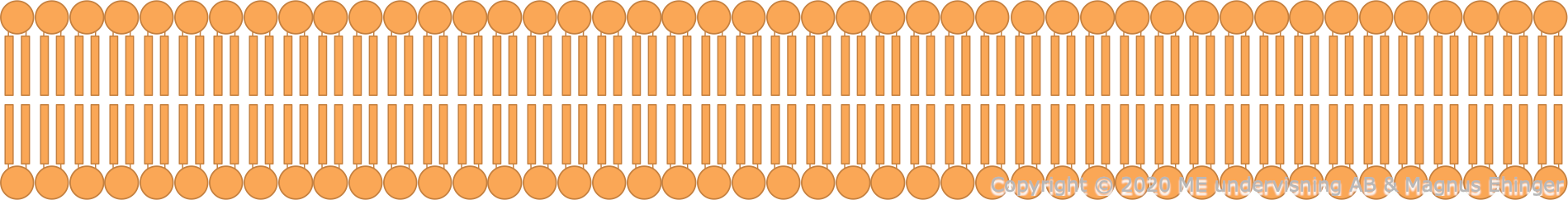 The cell membrane is a double layer of phospholipids.
The cell membrane is a double layer of phospholipids.
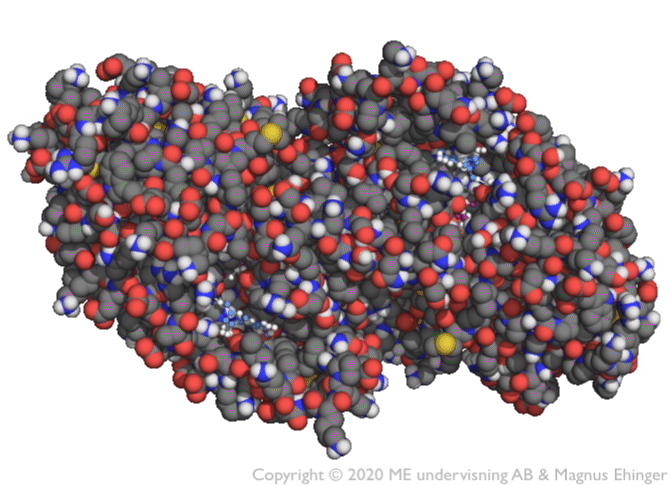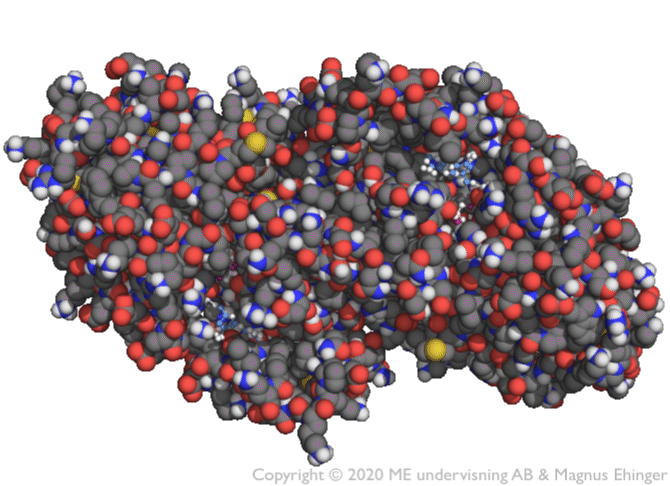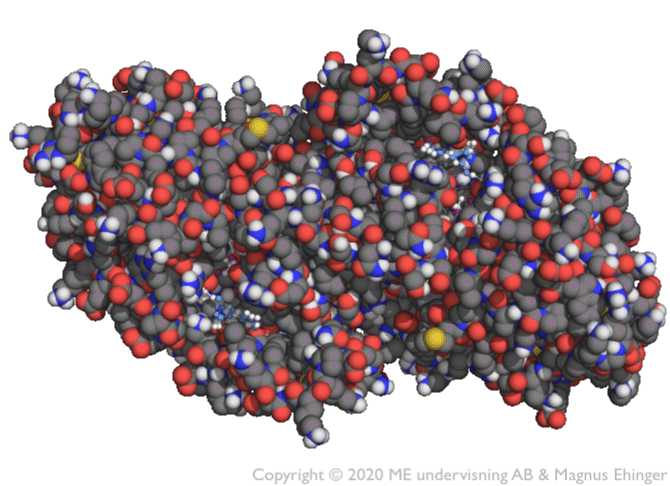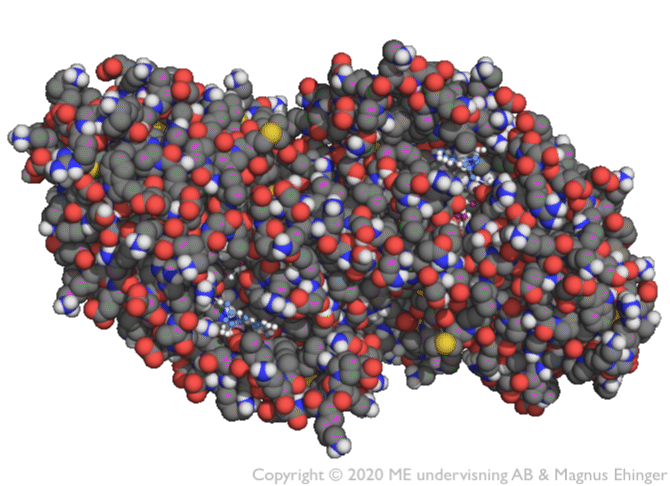
Nucleic acids
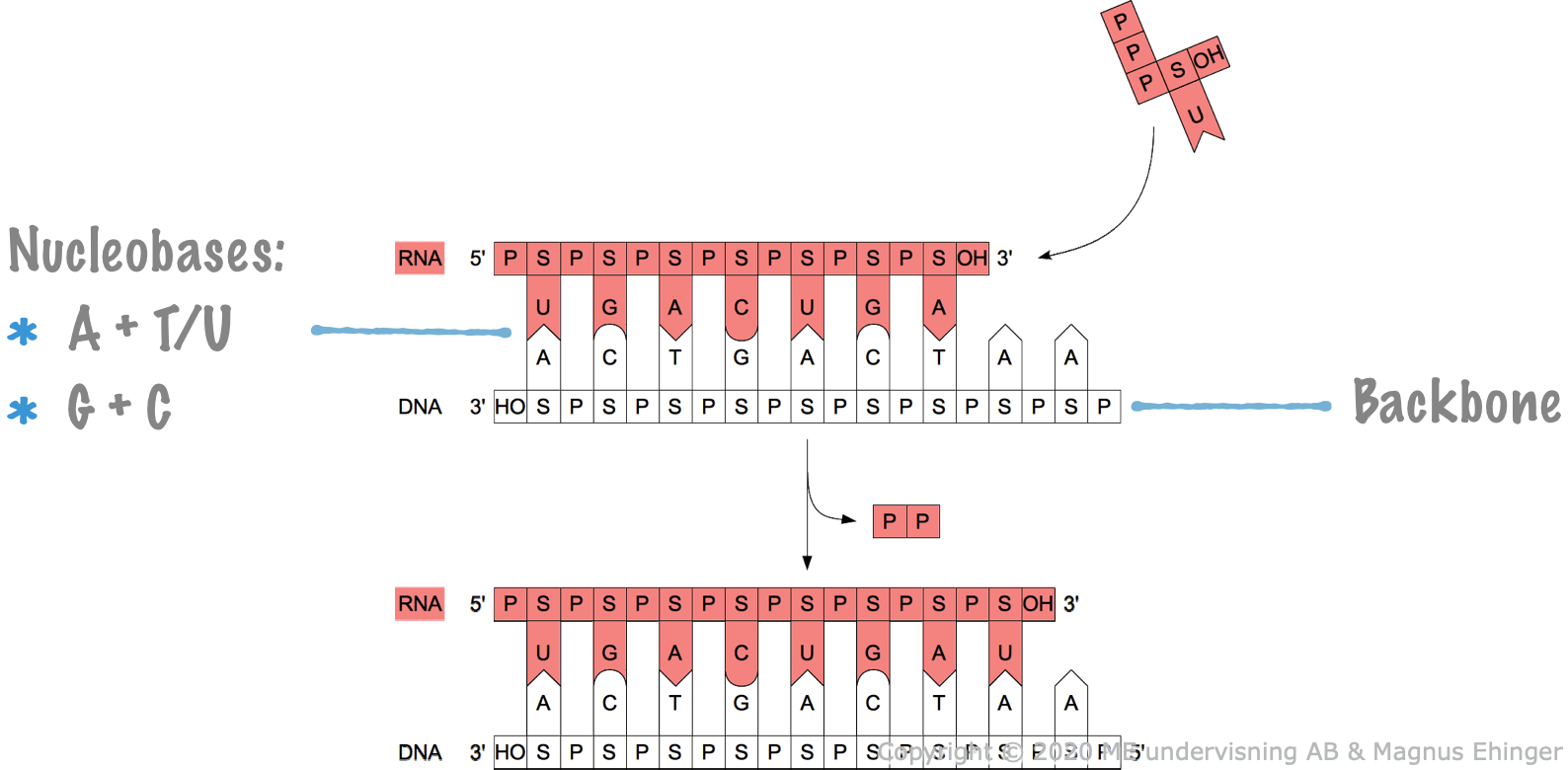 Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides.
Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides.
The nucleic acids are DNA and RNA.
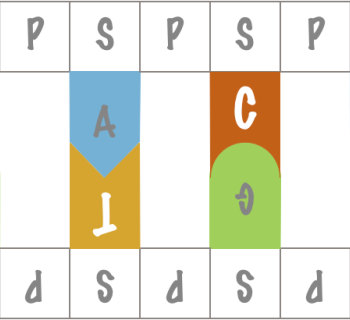
Backbone
- Alternating sugar (S) and phosphate (P) residues.
Nucleobases
- A always base pairs with T (in RNA, T is replaced with U), and vice versa.
- G always base pairs with C